
GST Tax Reform in India Is Beneficial to The Government?
RELEASE DATE: Jul 2024 Author: Spherical InsightsRequest Free Sample Speak to Analyst
Market Overview
The Goods and Service Act (GST) is an indirect tax that is imposed on the supply of goods and services. It is the descendant of Value Added Tax (VAT) also called consumption tax which was formerly used in India to tax various goods and services. This tax came into existence on 1st July 2017 because of the enactment of the One Hundred and First Amendments to the constitution of India by the Government of India. GST removed the existing numerous taxes imposed by the central or state government. It is said to be a comprehensive, multistage, and destination-based tax that is imposed on every value addition. The GST is categorized into 5 separate tax stages for the collection of tax which are 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. However, certain products like petroleum, alcoholic beverages, and electricity are not taxed under the GST regime instead they are taxed independently by the individual state governments of various states.
The GST is said to be a comprehensive, destination-based, and multistage tax due to the following reasons.
Multi-stage
GST is said to be a multi-stage tax because it is collected at every stage of production right from the procurement of raw materials to the final sale of the product to the consumer. Understand why GST is referred to as a multi-stage tax by reviewing the flowchart provided below.
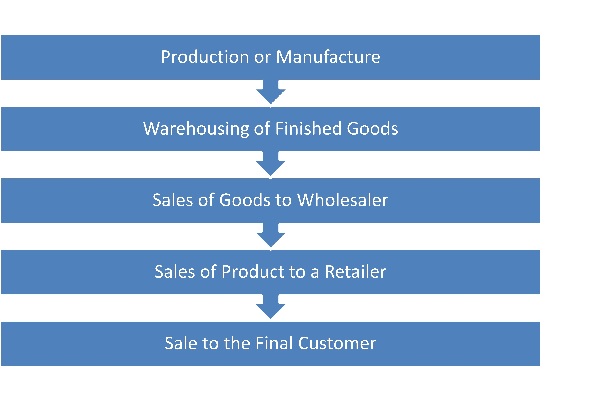
Value Addition
There is some value added to the finished good at each of these stages, GST is imposed at each instance of value addition. By, studying the flow chart below it provides a clear interpretation of multi-stage taxation and the addition of value in the jurisdiction of the GST.
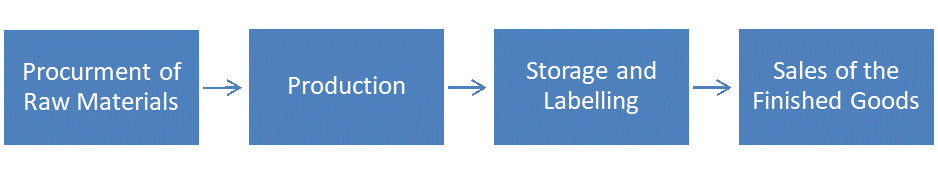
Stage 1: Addition of value to the raw material right from its procurement to the manufacturing process.
Stage 2: There is a certain value addition to the raw material when it goes through the production process which turns it into a particular product.
Stage 3: Labelling of the product in the stockroom adds more distant value to the product.
Stage 4: The labeled products are sold to the retailer which markets the product to the end user adding further value to the product.
Vital features of GST
- One Nation, One Tax- Numerous indirect taxes which was imposed by the Central and State governments were replaced by the GST. Indirect taxes like excise duty, service tax, and value-added tax (VAT) have been abolished by the addition of GST. This has brought consistency in the tax structure of India.
- Dual Structure- GST works in a binary process, which includes the Central GST (CGST) imposed by the Central Government and the State GST (SGST) imposed by the State Government. On the occasion of inter-state transactions, Integrated GST (IGST) is applied which is collected by both the Central and State Governments.
- Anti-Profiteering Measures- This is a procedure to stop companies from making undue profits with the implementation of GST which includes taking advantage of the circumstances to make a profit by over-pricing the things consumers need. To tackle this situation, the government has established the National Anti-Profiteering Authority (NAA) which observes and makes sure that the companies do not take part in unfair pricing practices.
- Greater Clarity and Compliance- GST works by bringing greater tax obedience by bringing more business into the bigger economy. This translucent nature of the tax system alongside the digitalization process of maintaining the electronic records assists in inhibiting tax evasion to promote tax obedience.
The Government of India reported that total GST revenue collection was Rs1.73 lakh crore ($21.1 billion USD) in May 2024, with a 10% year-over-year growth. In 2024-25 (January to May 2024), gross GST revenue collection totalled Rs3.83 lakh crore ($45.7 billion USD), representing an 11.3% year-on-year increase. Net revenue collection for the fiscal year 2024-25 (through May 2024) has increased to 11.6%.
Categorization of the May 2024 GST Revenue Collections
- Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) stood at Rs32,409 crore;
- State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) is at Rs40,265 crore;
- Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) is equivalent to Rs87,781 crore which includes Rs39,879 crore collected on imported goods;
- Cess Tax collections stood at Rs12,284 crore which includes Rs1,076 crore accumulated by imported goods.
Categorization of GST collections for the financial year of 2024-25 up to May 2024 are as follows:
- Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) stood at Rs76,255 crore;
- State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) is at Rs93,804 crore;
- Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) is equivalent to Rs1,87,404 crore, including Rs77,706 crore collected on imported goods;
- Cess Tax collections stood at Rs25,544 crore which includes Rs2,084 crore accumulated by imported goods.
About the Spherical Insights & Consulting
Spherical Insights & Consulting is a market research and consulting firm which provides actionable market research study, quantitative forecasting and trends analysis provides forward-looking insight especially designed for decision makers and aids ROI.
Which is catering to different industry such as financial sectors, industrial sectors, government organizations, universities, non-profits and corporations. The company's mission is to work with businesses to achieve business objectives and maintain strategic improvements.
CONTACT US:
For More Information on Your Target Market, Please Contact Us Below:
Phone: +1 303 800 4326 (the U.S.)
Phone: +91 90289 24100 (APAC)
Email: inquiry@sphericalinsights.com, sales@sphericalinsights.com
Contact Us: https://www.sphericalinsights.com/contact-us
Need help to buy this report?