Japan Waste-To-Energy Market Size, Share, and COVID-19 Impact Analysis, By Technology (Incineration and Gasification), By End-User (Power Generation and Heat Generation), and Japan Waste-To-Energy Market Insights, Industry Trend, Forecasts to 2033.
Industry: Energy & PowerJapan Waste-To-Energy Market Insights Forecasts to 2033
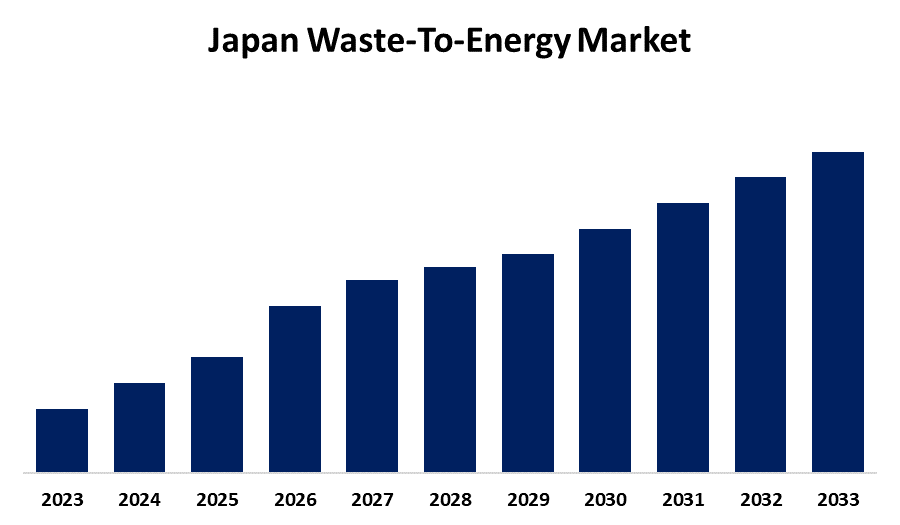
- The Japan Waste-To-Energy Market is Growing at a CAGR of 12.62% from 2023 to 2033
- The Japan Waste-To-Energy Market Size is Expected to Hold a Significant Share by 2033
Get more details on this report -
The Japan Waste-To-Energy Market is Anticipated to Expected to Hold a Significant Share by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.62% from 2023 to 2033
Market Overview
The recycling of waste materials into useable energy sources, such as heat, electricity, or biofuels, is the focus of the waste-to-energy (WTE) market in Japan. This is essential for managing the nation's rising waste output while also meeting its energy demands. Several technologies, including incineration, anaerobic digestion, and gasification, are included in the WTE market. These technologies reduce landfill trash and produce clean energy, which promotes environmental sustainability. The growth of the WTE market in Japan is influenced by several variables. There is an increasing need for WTE technology to lessen the negative environmental effects of garbage due to the nation's limited waste disposal territory. The Japanese government's policies, including the Waste Management and Public Cleansing Act, the Feed-in Tariff scheme, and the government's plan for carbon neutrality by 2050, are promoting the use of Waste Treatment and Energy (WTE) technologies due to their environmental sustainability and carbon emission reduction benefits. These policies aim to increase waste reduction and energy recovery, promote recycling and separation of waste, and stimulate long-term growth in the WTE market. These policies contribute to the country's commitment to sustainable waste management practices.
Report Coverage
This research report categorizes the market for the Japan waste-to-energy market based on various segments and regions forecasts revenue growth and analyzes trends in each submarket. The report analyses the key growth drivers, opportunities, and challenges influencing the Japan waste-to-energy market. Recent market developments and competitive strategies such as expansion, product launch, and development, partnership, merger, and acquisition have been included to draw the competitive landscape in the market. The report strategically identifies and profiles the key market players and analyses their core competencies in each sub-segment of the Japan waste-to-energy market.
Japan Waste-To-Energy Market Report Coverage
| Report Coverage | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year: | 2023 |
| Market Size in 2023 : | USD XX Billion |
| Forecast Period: | 2023 – 2033 |
| Forecast Period CAGR 2023 – 2033 : | 12.62% |
| 023 – 2033 Value Projection: | USD XX Billion |
| Historical Data for: | 2019-2022 |
| No. of Pages: | 220 |
| Tables, Charts & Figures: | 100 |
| Segments covered: | By Technology, By End-User |
| Companies covered:: | Chiyoda Corporation, Hitachi Zosen Corporation, JFE Engineering Corporation, Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd., LanzaTech Global. Inc., Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd., Sekisui Chemical Co., Others, and |
| Pitfalls & Challenges: | COVID-19 Impact, Challenges, Future, Growth, & Analysis |
Get more details on this report -
Driving Factors
The waste-to-energy (WTE) market in Japan is dominated by several fundamental variables. A major contributing reason is the lack of land appropriate for landfills, which forces the country to choose other waste management strategies. WTE technology offers an alternative, hence advancing environmental sustainability to preserve landfill space and generate renewable energy. The increasing need for energy also encourages the development of waste-to-energy technologies, especially as Japan looks to reduce its dependency on imported fossil fuels. Additionally, Japan's commitment to becoming carbon neutral by 2050 encourages investments in greener energy sources like WTE, which emits fewer emissions than traditional waste disposal methods.
Restraining Factors
The high initial capital investment in waste-to-energy (WTE) plants poses challenges for small towns and private financiers. A complicated regulatory structure and a slow approval process can hinder implementation. Public opposition to incineration due to air pollution and health concerns can discourage the widespread use of specific WTE technologies. These hurdles must be overcome for future market growth and scalability in Japan.
Market Segmentation
The Japan waste-to-energy market share is classified into technology and end-user.
- The incineration segment accounted for the largest share in 2023 and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
The Japan waste-to-energy market is segmented by technology into incineration and gasification. Among these, the incineration segment accounted for the largest share in 2023 and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. Incineration, a waste-to-energy conversion technology in Japan, involves burning waste materials at high temperatures to produce electricity or heat, reducing waste volume. Japan's advanced infrastructure for incineration is widely used due to its effectiveness in processing large amounts of waste.
- The power generation segment accounted for the highest share in 2023 and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
Based on the end-user, the Japan waste-to-energy market is divided into power generation and heat generation. Among these, the power generation segment accounted for the highest share in 2023 and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. Japan's WTE projects primarily focus on producing electricity from waste burning, with incineration being the dominant technology. This solution addresses waste disposal and energy requirements, addressing Japan's high electricity demand and low natural resources. Waste-to-energy power generation is a significant way to increase local electricity supply, despite the challenges of waste management.
Competitive Analysis:
The report offers the appropriate analysis of the key organizations/companies involved within the Japan waste-to-energy market along with a comparative evaluation primarily based on their product offering, business overviews, geographic presence, enterprise strategies, segment market share, and SWOT analysis. The report also provides an elaborative analysis focusing on the current news and developments of the companies, which includes product development, innovations, joint ventures, partnerships, mergers & acquisitions, strategic alliances, and others. This allows for the evaluation of the overall competition within the market.
List of Key Companies
- Chiyoda Corporation
- Hitachi Zosen Corporation
- JFE Engineering Corporation
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd.
- LanzaTech Global. Inc.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
- Sekisui Chemical Co.
- Others
Key Target Audience
- Market Players
- Investors
- End-users
- Government Authorities
- Consulting And Research Firm
- Venture capitalists
- Value-Added Resellers (VARs)
Recent Developments
- In September 2024, LanzaTech and Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd. have signed a Master License Agreement to develop multiple commercial-scale waste-to-ethanol plants across Japan. This collaboration aims to convert municipal solid waste (MSW) and industrial solid waste into ethanol using LanzaTech's bioprocessing platform.
Market Segment
- This study forecasts revenue at Japan, regional, and country levels from 2020 to 2033. Spherical Insights has segmented the Japan waste-to-energy market based on the below-mentioned segments
Japan Waste-To-Energy Market, By Technology
- Incineration
- Gasification
Japan Waste-To-Energy Market, By End-User
- Power Generation
- Heat Generation
Need help to buy this report?