Global Short-Acting Insulin Market Size, Share & Trends, COVID-19 Impact Analysis Report, Segmented by Drug (Apidra (Glulisine), Novolog/Novorapid, Humalog (Lispro), Novolin (Actrapid), Insuman, Humulin, FIASP, and Admelog) and Geography (North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia Pacific, and Middle-East and Africa) - Market Size Statistics & Forecasting To 2030
Industry: HealthcareGlobal Short-Acting Insulin Market Size: Is Segmented, By Information, By Drug (Novolog, Humalog, Humulin), By Regional Analysis, And Forecast Till 2030.
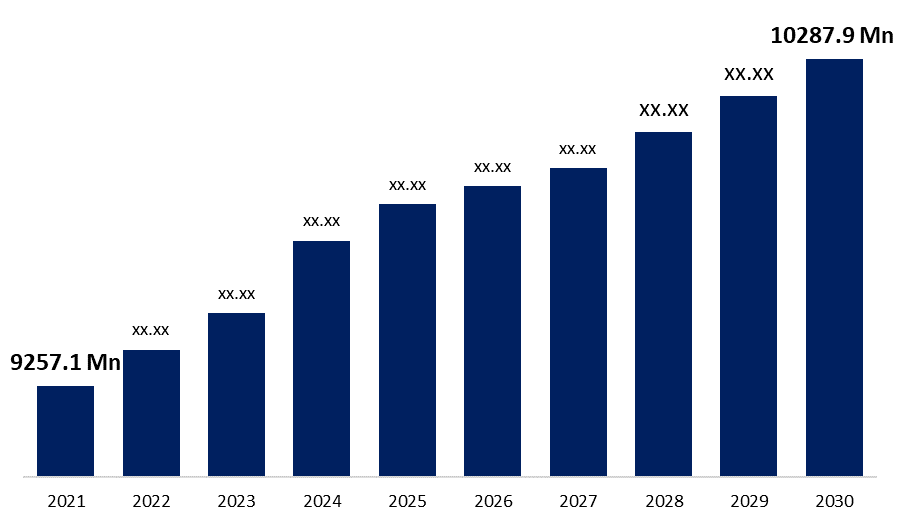
The Global Market For Short-Acting Insulin will reach USD 10287.9 Million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 1.18% from USD 9257.1 Million in 2021.
Get more details on this report -
MARKET OVERVIEW
The market for rapid-acting insulin is dominated by three companies: Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, and Eli Lilly. Each of these companies has built its brand name in the marketplace. To access the local markets, however, these firms must exert substantial effort due to the severe competition there. Consequently, they utilise powerful competitive techniques to bolster their market position. Motivated by the market's high profitability, numerous generic insulin (biosimilars) manufacturers and significant firms striving to launch unique goods are abundant. This is why the demand for short-acting insulin attracts the attention of substantial business people seeking to enter a lucrative market.
Global Short-Acting Insulin Market Report Coverage
| Report Coverage | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year: | 2021 |
| Market Size in 2021: | USD 9257.1 Million |
| Forecast Period: | 2021-2030 |
| Forecast Period CAGR 2021-2030 : | 1.18% |
| 2030 Value Projection: | USD 10287.9 Million |
| Historical Data for: | 2017-2020 |
| No. of Pages: | 170 |
| Tables, Charts & Figures: | 108 |
| Segments covered: | Is Segmented, By Information, By Drug (Novolog, Humalog, Humulin), By Regional Analysis, And Forecast Till 2030. |
| Companies covered:: | Novo Nordisk AS, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, and Company, Verily, Sensile, etc. |
| Growth Drivers: | Initiatives undertaken by the government to avoid the spread of diabetes and the prevalence of diagnosed cases are stimulating the R&D of the aforementioned market |
| Pitfalls & Challenges: | The High Treatment Cost attributable to the Price Increase of Insulin could be a significant limitation for the global market for rapid-acting insulin |
Get more details on this report -
SHORT-ACTING INSULIN MARKET DRIVERS –
Initiatives undertaken by the government to avoid the spread of diabetes and the prevalence of diagnosed cases are stimulating the R&D of the aforementioned market.
At the federal, state, and municipal levels of government, government policies play a vital role in promoting the quality and safety of healthcare. The objective of government regulations and environmental changes is to make healthy behaviours more available or desirable while making detrimental exposures more difficult or illegal. Diabetes is a chronic illness that affects about 30 million individuals. To guarantee that people in every area have unrestricted access to low-cost, high-quality health insurance, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) of 2010 established a model of shared responsibility between the government, employers, and individuals.
The prevalence of diagnosed instances encourages the research and development of the market-driving short-acting insulins.
According to WHO, there are over 400 million diabetics worldwide, and its treatment accounts for over 12% of global healthcare expenses. American Diabetes Association (ADA) reported a rise in newly diagnosed Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes cases in the United States, with about 40,000 new Type 1 diabetes cases registered annually. Many patents for major branded insulin products are expected to expire within the next decade, and diabetes monitoring and prevention organisations such as the ADA are investing substantial resources in research of biosimilars or insulins to improve the quality of medical services and the efficacy of administered treatments. In 2018, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) supported 318 new and ongoing projects targeting all types of diabetes and its myriad complications through various scientific methods.
Global interest in creating and exploiting this insulin is increasing. Biosimilar insulins can dramatically cut the costs associated with diabetes treatment while enhancing insulin treatment accessibility and market competitiveness. Currently, two biosimilar insulins have been approved, utilising the old approach in the United States. They are Basaglar (Lilly), an approved replacement for Glargine (Lantus, Sanofi) in 2015, and Admelog (Sanofi), an approved replacement for Lispro in 2017. (Humalog, Lilly).
RESTRAINTS ON THE SHORT-ACTING INSULIN MARKET
The High Treatment Cost attributable to the Price Increase of Insulin could be a significant limitation for the global market for rapid-acting insulin.
There are five major insulin types: ordinary insulin, NPH, rapid-acting analogues, basal analogues, and pre-mixed insulin. Insulin analogues are often much more expensive than ordinary insulin or NPH because their amino acid sequences are bioengineered to attain the necessary chemical characteristics. Since the entry of the twenty-first century, the price of insulin has multiplied as a result of multiple factors. The lack of competition from generics is one of the key reasons why insulin costs continue to rise. Insulin is a medicinal biological product and not a chemically created molecule; hence it cannot be manufactured in a generic form. Moreover, the scientific and financial constraints involved with the development of biosimilars, such as the various research phases and demanding clinical trials, limit the practicality of a prospective insulin alternative.
Insulin prices have soared and show no signs of stabilising, as patents and other legal constraints prohibit the entry of new players with equivalent product offerings. Sanofi has submitted 74 patent applications for Lantus alone, meaning that the business has created the potential for a 37-year monopoly. At any time, drug corporations may impose a price increase; hence, they must be regulated via the implementation of reforms to prevent price increases. In response to the rise in insulin prices, some private insurance companies are independently working to cap consumers' out-of-pocket insulin costs. The government has taken numerous measures to boost the accessibility and affordability of insulin. Insulin is inaccessible to low-income communities as daily therapy for Type 1 diabetes, hence limiting the market's growth potential and subjecting a substantial section of the diabetic population to major health risks.
OPPORTUNITIES IN THE GLOBAL SHORT-ACTING INSULIN MARKET –
Rapid Innovations in the production and study of insulin have generated an abundance of options.
Even though the need is driven by the increasing number of insulin users worldwide, in most locations, only a limited number of enterprises can supply this demand. Consequently, only insulin makers have the ability to establish prices. Even government end-users have little or no control over prices. Since the production of insulin is severely regulated by patents and other legal infractions, it is forbidden for new businesses to produce identical drugs before the patent expires. This illustrates the dominance of a limited number of market actors that strive to maximise profit by using their technological expertise. Earlier, there were no alternatives to rapid-acting insulins. Recent emphasis on the creation of less-priced biosimilars has disrupted the traditional market dynamic, opening for the development of a novel class of insulins. However, biosimilars are still in their infancy, and there are now only a few of these treatments on the market. The recently prepared FDA resolution is widely anticipated to boost biosimilars' research and development (R&D) and advocate their adoption as less expensive alternatives for the treatment of diabetes. Through their established supply chain and branding, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, and Lilly have built a monopoly on the market, resulting in considerable global market penetration. These companies interact with a variety of administrative and health authorities to design and implement competitive strategies, creating an enormous opportunity for newcomers and industry pros to earn business through the aforementioned market area.
SEGMENTATION OF THE GLOBAL SHORT-ACTING INSULIN MARKET
The Global Short-Acting Insulin Market is separated by drug type, which is further subdivided into Novolog, Humalog, and Humulin. Novolog medicine dominates the global insulin market with a market share of USD 2651.2 million in 2021 and is projected to reach USD 2694.5 million by 2030 with a CAGR of 0.18%. In combination with mealtime insulin, Novolog is a rapid-acting insulin. It was intended to attain pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic features that more closely approximate the physiological mealtime response of insulin in a non-diabetic individual. The Humalog segment is the second largest, with a market value of USD 2,462.7 million in 2021 and a projected value of USD 1,966 million by 2030, at a CAGR of -2.47%. The third and fastest-growing segment is Humulin, which had a market value of USD 1283.7 million in 2021 and is anticipated to reach USD 1564.1 million by 2030 at a CAGR of 2.22%.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS OF THE WORLDWIDE MARKET FOR SHORT-ACTING INSULIN –
Get more details on this report -
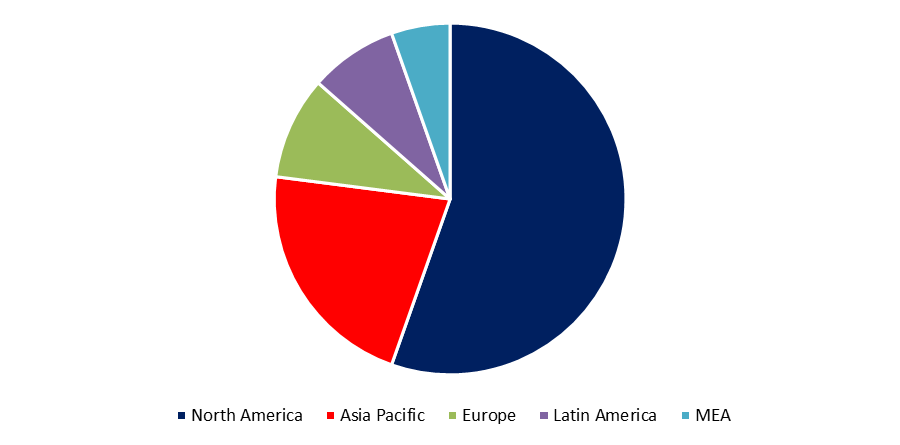
Primarily, the global market for rapid-acting insulin is classified into North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. With a market size of USD 481.94 million in 2021 and projected to reach USD 588.7 million by 2030 at a CAGR of 2.25%, North America dominates the market. As the most developed and largest economy in the world, North America possesses world-class healthcare facilities, which is the primary basis for its market supremacy. The Asia-Pacific area is ranked second in the aforementioned segmentation, with a market value of USD 48.22 million in 2021 and projected to reach USD 68.8 million by 2030 at a CAGR of 4.04%. The development of the Asia-Pacific region is attributable to the extraordinary expansion of the healthcare industry in the region, which has had a remarkable rate of expansion. Europe ranks third with a revenue of USD 9.05 million in 2021 and projected growth to USD 13.21 million by 2030, a CAGR of 4.3%. Europe boasts a number of important manufacturers and research institutions that contribute to the region's overall revenue output.
KEY COMPETITORS IN THE GLOBAL SHORT-ACTING INSULIN MARKET –
The prominent competitors in the global short-acting insulin market are – Novo Nordisk AS, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, and Company, Verily, Sensile, etc.
RECENT ADVANCES BY MAJOR PLAYERS –
• In January 2020, Novo Nordisk's Ozempic, a once-weekly treatment for type 2 diabetes, was approved for consumption by patients worldwide.
• In September 2019, Sanofi announced a collaboration with Verily and Sensile Medical to develop an all-in-one insulin patch pump.
• In June 2020, Eli Lilly & Company announced a USD 400 million investment to expand their production capacity.
SEGMENTATION OF GLOBAL SHORT ACTING INSULIN MARKET –
By Drug –
- Novolog
- Humalog
- Humulin
By Region:
- North America
- Asia- Pacific
- Europe
- Middle-East & Africa
Need help to buy this report?